A network topology is a schematic description of a network configuration, connecting various nodes (sender and receiver) through lines of connection. A topology is a schematic diagram that shows how networks are physically and logically connected. Physical topology is the physical layout of workstations, nodes and cables in a network; While logical topology is the way information flows between different components. Network topology is therefore the configuration of different components of a computer network. Details of network topologies are given below and are presented in Figs
1. Bus Topology :
In this type of topology all the computers are connected to the terminator at each end by a cable of the same length. Bus topology is the simplest and most widely used local field network design. Only one and only one computer at a time can send a message. It transmits data in only one direction and each device is connected by a single cable. So it affects the speed of the network. It is cost effective and requires a minimal amount of cable compared to other topologies. It is commonly used in small networks and is very easy to understand. But it is slow and if the main cable fails, the whole network fails.
2. Star Topology :
The Star Network is often used to connect one or more small computers or peripheral devices to a large host computer or CPU. Each computer on the Star Network interacts with a central hub that sends the message back to all computers or just the destination computer. Each node has a dedicated connection to the central hub. It's faster with fewer nodes and less network traffic. Easy to troubleshoot and easy to set up. But the cost of installation is high and it is also expensive to use. If the host computer fails, the entire network is affected.
3. Token ring :
A token ring network is a local area network (L) in which all computers are connected in a ring or star topology and a bit- or token passing scheme is used to prevent data from colliding between two computers. Who wants to send messages at the same time. The token ring protocol was developed by IBM. The method access method used includes token passing. In the token ring, computers are connected so that the signal travels from one computer to another in a logical ring around the network.
4. Ring Topology :
In this type of topology, workstations are connected in a circle using cable segments. In this layer each node is physically connected to only two other nodes, i.e., the adjacent pair directly connected to the workstation. The ring topology can function without a server. Ring topology can be maximized when system requirements are modest and workstations are scattered.
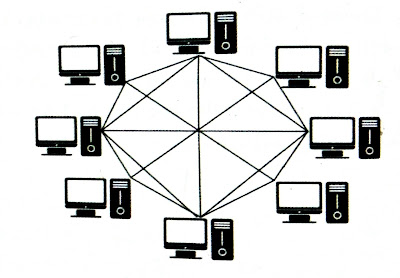
5. Mesh Topology :
It is a type of network setup where every computer and network devices are connected to each other. Most large backbone networks use a mesh topology in which a single switch or router failure can result in a large portion of the network going down. A mesh network topology is a decentralized design in which each node on the network is connected to at least two other nodes. The mesh network can use full mesh topology or partial mesh topology. In a complete mesh topology, each network node is connected to all other nodes in the network. In a partial mesh topology, at least one node connects directly to each other node while the other can only connect to the nodes with which they exchange data on a frequent basis.
6. Tree topology :
Tree topology, also known as hierarchical topology, uses two or more star networks connected together. It can also employ a combination of bus and star topology. This topology divides the network into several layers of network. It has root nodes, intermediate nodes and end nodes. Tree network topology is ideal when workstations are located in groups, each group occupying a relatively small physical area. One example is the university campus in which each and every building has its own star network, and all central computers are connected to a campus-wide system. It's easy to add or remove workstations from every star network. The entire star network can be added to or removed from the bus.
Network Protocols
Network protocol defines the rules and conventions for communication between network devicesand how they connected with eachther. Network protocols include methods for identifying and creating devices with each other. The following are several protocols
1. FTP :
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is the most widely used protocol for file transfer over a network. FTP uses TCP / IP for communication.
2. PPP :
PPP means point-to-point protocol. It is a more developed protocol than SLIP, as long as it transfers additional data, which is more suitable for data transmission over the Internet.
3. TCP / IP :
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and IP (Internet Protocol) are two different processes that are often linked together. Combining different protocols is common because the functions of different protocols can be complementary so they carry out several complete functions simultaneously.
4. HTTP :
Hypertext is a well-organized documentation system that uses hyperlinks to link pages in text documents. HTTP (i.e. Hypertext Transfer Protocol) works on the client server model.
5. HTTPS :
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is a communication protocol for secure communication over a computer network.
6. Slip :
Serial line internet protocol is the result of the integration of modern protocols before the TCP / IP protocol claims. It is a simple internet link protocol that has no address or error control, which is why it is becoming obsolete faster than PPP.
You will learn more about the protocol in the next blog.







0 Comments